1、ArrayList 简述 Java ArrayList是List接口的可调整大小的数组 实现,这意味着它以默认大小开始,并在将更多数据添加到数组列表时自动扩容 。 除了实现List接口之外,此类还提供了一些方法来操作内部用于存储列表的数组的大小。
ArrayList不是线程安全 的,多线程环境下可以考虑用 List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(…)); 函数返回一个线程安全的ArrayList类,也可以使用concurrent并发包下的CopyOnWriteArrayList类。
ArrayList 的iterator和listIterator方法返回的迭代器是快速失败的:如果在创建迭代器之后的任何时候对列表进行结构修改,除了通过迭代器自己的remove或add方法之外,迭代器将抛 出ConcurrentModificationException。 因此,在并发修改的情况下,迭代器快速失败,而不是在未来的未确定时间冒任意,非确定性的风险 。
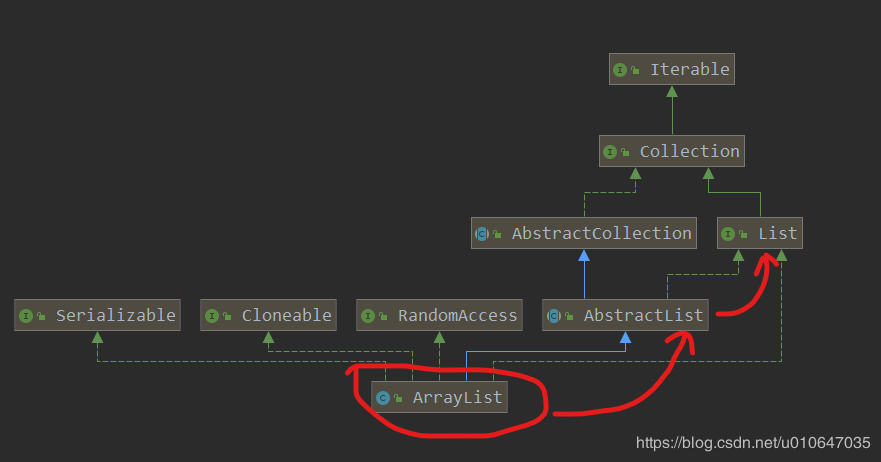
2、ArrayList 类图
ArrayList 继承 了 AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable这些接口。
ArrayList** 实现了** RandmoAccess 接口,即提供了随机访问功能。RandmoAccess是java中用来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的。在ArrayList中,我们即可以通过元素的索引快速获取元素对象;这就是快速随机访问。
ArrayList** 实现了** Cloneable接口,即覆盖了方法clone(),能被克隆。
ArrayList 实现了 java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着ArrayList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
ArrayList与Vector不同 ,ArrayList 中的操作不是线程安全的。所以,建议在单线程中才使用ArrayList,而在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList。
3、ArrayList 构造函数 ArrayList 提供了三个构造函数,分别如下:
3.1、ArrayList() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ArrayList 默认构造函数会初始化一个容量为10 的空列表,这也就意味着ArrayList的默认大小为10. public ArrayList () { this .elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }
3.2、ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 该构造函数接受一个int类型的数值来初始化 ArrayList,如果指定的初始容量大小为负数,将会抛出异常 IllegalArgumentException
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public ArrayList (int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0 ) { this .elementData = new Object [initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0 ) { this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity); } }
3.3、ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public ArrayList (Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0 ) { if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }
4、ArrayList 源码解析4、ArrayList 源码解析 4.1、私有字段说明 ArrayList包含了两个重要的对象:elementData 和 size。
1)elementData 是”Object[]类型的数组”,它保存了添加到ArrayList中的元素。实际上,elementData是个动态数组,我们能通过构造函数 ArrayList(int initialCapacity)来指定它的初始容量为initialCapacity;
如果通过不含参数的构造函数ArrayList()来创建ArrayList,则elementData的容量默认是10。elementData数组的大小会根据ArrayList容量的增长而动态的增长,具体的增长方式,请参考源码分析中的ensureCapacity()函数。
2) size 则是动态数组的实际大小。
4.1.1、AbstractList>modCount 子类使用这个字段是可选的,若子类希望提供fail-fast(快速失败) iterators或者list iterators 可以在方法里使用该方法。
这个变量用于快速判断该实例是否有变化,若在进行迭代的时候有变更,那么就抛出一个并发修改异常(ConcurrentModificationException)。
1 2 3 java.util.AbstractList: protected transient int modCount
4.1.2、DEFAULT_CAPACITY 1 2 3 4 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ;
4.1.3、EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 1 2 3 4 5 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
4.1.4、DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 1 2 3 4 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
4.1.5、elementData 1 2 3 4 5 transient Object[] elementData;
4.1.6、size 4.1.7、MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 1 2 3 4 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 ;
4.2、ArrayList 方法源码解析4.2、ArrayList 方法源码解析 4.2.1、public void trimToSize()4.2.1、public void trimToSize() 将此ArrayList实例的容量调整为列表的当前大小。 应用程序可以使用此操作来最小化ArrayList实例的存储。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public void trimToSize () { modCount++; if (size < elementData.length) { elementData = (size == 0 ) ? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA : Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } }
4.2.2、public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) 如有必要,增加此ArrayList实例的容量,以确保它至少可以容纳由minCapacity参数指定的元素数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public void ensureCapacity (int minCapacity) { int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) ? 0 : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; if (minCapacity > minExpand) { ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } } private void ensureExplicitCapacity (int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow (int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1 ); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0 ) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0 ) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity (int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0 ) throw new OutOfMemoryError (); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }
4.2.3、public int size() 返回此列表中的元素数。
1 2 3 public int size () { return size; }
4.2.4、public boolean isEmpty() 如果此列表不包含任何元素,则返回true。
1 2 3 public boolean isEmpty () { return size == 0 ; }
4.2.5、public boolean contains(Object o) 如果此列表包含指定的元素,则返回true。当且仅当此列表包含至少一个元素e时才返回true(o == null?e == null:o.equals(e))。
1 2 3 public boolean contains (Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0 ; }
4.2.6、public int indexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中第一次出现的指定元素的索引,如果此列表不包含该元素,则返回-1。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public int indexOf (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null ) return i; } else { for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1 ; }
4.2.7、public int lastIndexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中指定元素最后一次出现的索引,如果此列表不包含该元素,则返回-1。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public int lastIndexOf (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int i = size-1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (elementData[i]==null ) return i; } else { for (int i = size-1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1 ; }
4.2.8、public Object clone()4.2.8、public Object clone() 返回此ArrayList实例的副本。(元素本身不会被复制。)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public Object clone () { try { ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super .clone(); v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); v.modCount = 0 ; return v; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { throw new InternalError (e); } }
4.2.9、public Object[] toArray()4.2.9、public Object[] toArray() 以适当的顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)返回包含此列表中所有元素的数组。返回的数组将是“安全的”,因为此列表不会保留对它的引用。 (换句话说,此方法必须分配一个新数组)。 因此调用者可以自由修改返回的数组。
1 2 3 public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); }
4.2.10、public T[] toArray(T[] a)4.2.10、public T[] toArray(T[] a) 以适当的顺序返回包含此列表中所有元素的数组(从第一个元素到最后一个元素); 返回数组的类型是指定数组的运行时类型。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { if (a.length < size) return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass()); System.arraycopy(elementData, 0 , a, 0 , size); if (a.length > size) a[size] = null ; return a; }
4.2.11、public E get(int index)4.2.11、public E get(int index) 返回此列表中指定位置的元素。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public E get (int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } private void rangeCheck (int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } E elementData (int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; }
4.2.12、public E set(int index, E element)4.2.12、public E set(int index, E element) 用指定的元素替换此列表中指定位置的元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public E set (int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; }
4.2.13、public boolean add(E e) 将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public boolean add (E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); elementData[size++] = e; return true ; } private void ensureCapacityInternal (int minCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity (int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity); } private static int calculateCapacity (Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; }
4.2.14、public void add(int index,E element) 将指定元素插入此列表中的指定位置。 将当前位于该位置的元素(如果有)和后续元素向右移动。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void add (int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1 , size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; }
4.2.15、public E remove(int index) 删除此列表中指定位置的元素。 将任何后续元素向左移动)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public E remove (int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; return oldValue; }
4.2.16、public boolean remove(Object o) 从此列表中删除指定元素的第一个匹配项(如果存在)。 如果列表不包含该元素,则不会更改。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public boolean remove (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null ) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } else { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } return false ; } private void fastRemove (int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; }
4.2.17、public void clear() 从此列表中删除所有元素。 此调用返回后,列表将为空。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public void clear () { modCount++; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null ; size = 0 ; }
4.2.18、public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 将指定集合中的所有元素按指定集合的迭代器返回的顺序附加到此列表的末尾。 如果在操作正在进行时修改了指定的集合,则此操作的行为是不确定的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public boolean addAll (Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); System.arraycopy(a, 0 , elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0 ; }
4.2.19、public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) 从指定位置开始,将指定集合中的所有元素插入此列表。 将当前位置的元素(如果有)和后续元素向右移动。 新元素将按照指定集合的迭代器返回的顺序出现在列表中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public boolean addAll (int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0 , elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0 ; }
4.2.20、protected void removeRange(int fromIndex,int toIndex) 从此列表中删除索引介于fromIndex(包含)和 toIndex(不包含)之间的所有元素。 将任何后续元素向左移动, 此调用通过(toIndex - fromIndex)元素缩短列表。如果toIndex == fromIndex,则此操作无效。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 protected void removeRange (int fromIndex, int toIndex) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - toIndex; System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex, numMoved); int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex); for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) { elementData[i] = null ; } size = newSize; }
4.2.21、public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) 从此列表中删除指定集合中包含的所有元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public boolean removeAll (Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, false ); } private boolean batchRemove (Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { final Object[] elementData = this .elementData; int r = 0 , w = 0 ; boolean modified = false ; try { for (; r < size; r++) if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; } finally { if (r != size) { System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r); w += size - r; } if (w != size) { for (int i = w; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null ; modCount += size - w; size = w; modified = true ; } } return modified; }
4.2.22、public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c): 从该列表中删除未包含在指定集合中的所有元素。
1 2 3 4 public boolean retainAll (Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, true ); }
4.2.23、public ListIterator listIterator(int index) 从列表中的指定位置开始,返回列表中元素的列表迭代器。 指定的索引指示初始调用next时将返回的第一个元素。 对previous的初始调用将返回指定索引减去1的元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public ListIterator<E> listIterator (int index) { if (index < 0 || index > size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ("Index: " +index); return new ListItr (index); } private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator <E> { ListItr(int index) { super (); cursor = index; } public boolean hasPrevious () { return cursor != 0 ; } public int nextIndex () { return cursor; } public int previousIndex () { return cursor - 1 ; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E previous () { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor - 1 ; if (i < 0 ) throw new NoSuchElementException (); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); cursor = i; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } public void set (E e) { if (lastRet < 0 ) throw new IllegalStateException (); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this .set(lastRet, e); } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } public void add (E e) { checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor; ArrayList.this .add(i, e); cursor = i + 1 ; lastRet = -1 ; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } }
4.2.24、public ListIterator listIterator() 返回此列表中元素的列表迭代器(按适当顺序)。
1 2 3 public ListIterator<E> listIterator () { return new ListItr (0 ); }
4.2.25、public Iterator iterator() 以适当的顺序返回此列表中元素的迭代器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 public Iterator<E> iterator () { return new Itr (); } private class Itr implements Iterator <E> { int cursor; int lastRet = -1 ; int expectedModCount = modCount; Itr() {} public boolean hasNext () { return cursor != size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next () { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException (); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); cursor = i + 1 ; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } public void remove () { if (lastRet < 0 ) throw new IllegalStateException (); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this .remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1 ; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void forEachRemaining (Consumer<? super E> consumer) { Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); final int size = ArrayList.this .size; int i = cursor; if (i >= size) { return ; } final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]); } cursor = i; lastRet = i - 1 ; checkForComodification(); } final void checkForComodification () { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } }
4.2.26、public List subList(int fromIndex,int toIndex) 返回指定fromIndex(包含)和toIndex(不包含)之间此列表部分的视图。如果fromIndex和toIndex相等,则返回的列表为空。 返回的列表由此列表支持,因此返回列表中的非结构更改将反映在此列表中,反之亦然。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 public List<E> subList (int fromIndex, int toIndex) { subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); return new SubList (this , 0 , fromIndex, toIndex); } static void subListRangeCheck (int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) { if (fromIndex < 0 ) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ("fromIndex = " + fromIndex); if (toIndex > size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ("toIndex = " + toIndex); if (fromIndex > toIndex) throw new IllegalArgumentException ("fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")" ); } private class SubList extends AbstractList <E> implements RandomAccess { private final AbstractList<E> parent; private final int parentOffset; private final int offset; int size; SubList(AbstractList<E> parent, int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) { this .parent = parent; this .parentOffset = fromIndex; this .offset = offset + fromIndex; this .size = toIndex - fromIndex; this .modCount = ArrayList.this .modCount; } public E set (int index, E e) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); E oldValue = ArrayList.this .elementData(offset + index); ArrayList.this .elementData[offset + index] = e; return oldValue; } public E get (int index) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); return ArrayList.this .elementData(offset + index); } public int size () { checkForComodification(); return this .size; } public void add (int index, E e) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); checkForComodification(); parent.add(parentOffset + index, e); this .modCount = parent.modCount; this .size++; } public E remove (int index) { rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index); this .modCount = parent.modCount; this .size--; return result; } protected void removeRange (int fromIndex, int toIndex) { checkForComodification(); parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex, parentOffset + toIndex); this .modCount = parent.modCount; this .size -= toIndex - fromIndex; } public boolean addAll (Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(this .size, c); } public boolean addAll (int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); int cSize = c.size(); if (cSize==0 ) return false ; checkForComodification(); parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c); this .modCount = parent.modCount; this .size += cSize; return true ; } public Iterator<E> iterator () { return listIterator(); } public ListIterator<E> listIterator (final int index) { checkForComodification(); rangeCheckForAdd(index); final int offset = this .offset; return new ListIterator <E>() { int cursor = index; int lastRet = -1 ; int expectedModCount = ArrayList.this .modCount; public boolean hasNext () { return cursor != SubList.this .size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next () { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= SubList.this .size) throw new NoSuchElementException (); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (offset + i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); cursor = i + 1 ; return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)]; } public boolean hasPrevious () { return cursor != 0 ; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E previous () { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor - 1 ; if (i < 0 ) throw new NoSuchElementException (); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (offset + i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); cursor = i; return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)]; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void forEachRemaining (Consumer<? super E> consumer) { Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); final int size = SubList.this .size; int i = cursor; if (i >= size) { return ; } final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (offset + i >= elementData.length) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { consumer.accept((E) elementData[offset + (i++)]); } lastRet = cursor = i; checkForComodification(); } public int nextIndex () { return cursor; } public int previousIndex () { return cursor - 1 ; } public void remove () { if (lastRet < 0 ) throw new IllegalStateException (); checkForComodification(); try { SubList.this .remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1 ; expectedModCount = ArrayList.this .modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } public void set (E e) { if (lastRet < 0 ) throw new IllegalStateException (); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this .set(offset + lastRet, e); } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } public void add (E e) { checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor; SubList.this .add(i, e); cursor = i + 1 ; lastRet = -1 ; expectedModCount = ArrayList.this .modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } } final void checkForComodification () { if (expectedModCount != ArrayList.this .modCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } }; } public List<E> subList (int fromIndex, int toIndex) { subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); return new SubList (this , offset, fromIndex, toIndex); } private void rangeCheck (int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= this .size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private void rangeCheckForAdd (int index) { if (index < 0 || index > this .size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private String outOfBoundsMsg (int index) { return "Index: " +index+", Size: " +this .size; } private void checkForComodification () { if (ArrayList.this .modCount != this .modCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } public Spliterator<E> spliterator () { checkForComodification(); return new ArrayListSpliterator <E>(ArrayList.this , offset, offset + this .size, this .modCount); } }
4.2.27、public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) 对Iterable的每个元素执行给定操作,直到处理完所有元素或操作抛出异常为止。 除非实现类另有指定,否则操作按迭代顺序执行。 操作抛出的异常会转发给调用者。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Override public void forEach (Consumer<? super E> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); final int expectedModCount = modCount; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final E[] elementData = (E[]) this .elementData; final int size = this .size; for (int i=0 ; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { action.accept(elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } }
4.2.28、public Spliterator spliterator() 在此列表中的元素上创建一个late-binding和fail-fast 的Spliterator。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 @Override public Spliterator<E> spliterator () { return new ArrayListSpliterator <>(this , 0 , -1 , 0 ); } static final class ArrayListSpliterator <E> implements Spliterator <E> { private final ArrayList<E> list; private int index; private int fence; private int expectedModCount; ArrayListSpliterator(ArrayList<E> list, int origin, int fence, int expectedModCount) { this .list = list; this .index = origin; this .fence = fence; this .expectedModCount = expectedModCount; } private int getFence () { int hi; ArrayList<E> lst; if ((hi = fence) < 0 ) { if ((lst = list) == null ) hi = fence = 0 ; else { expectedModCount = lst.modCount; hi = fence = lst.size; } } return hi; } public ArrayListSpliterator<E> trySplit () { int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1 ; return (lo >= mid) ? null : new ArrayListSpliterator <E>(list, lo, index = mid, expectedModCount); } public boolean tryAdvance (Consumer<? super E> action) { if (action == null ) throw new NullPointerException (); int hi = getFence(), i = index; if (i < hi) { index = i + 1 ; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)list.elementData[i]; action.accept(e); if (list.modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); return true ; } return false ; } public void forEachRemaining (Consumer<? super E> action) { int i, hi, mc; ArrayList<E> lst; Object[] a; if (action == null ) throw new NullPointerException (); if ((lst = list) != null && (a = lst.elementData) != null ) { if ((hi = fence) < 0 ) { mc = lst.modCount; hi = lst.size; } else mc = expectedModCount; if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) { for (; i < hi; ++i) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i]; action.accept(e); } if (lst.modCount == mc) return ; } } throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } public long estimateSize () { return (long ) (getFence() - index); } public int characteristics () { return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED; } }
4.2.29、public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) 删除此集合中满足给定谓词的所有元素。 在迭代期间或通过谓词抛出的错误或运行时异常将返回给调用者。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 @Override public boolean removeIf (Predicate<? super E> filter) { Objects.requireNonNull(filter); int removeCount = 0 ; final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet (size); final int expectedModCount = modCount; final int size = this .size; for (int i=0 ; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final E element = (E) elementData[i]; if (filter.test(element)) { removeSet.set(i); removeCount++; } } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0 ; if (anyToRemove) { final int newSize = size - removeCount; for (int i=0 , j=0 ; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) { i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i); elementData[j] = elementData[i]; } for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) { elementData[k] = null ; } this .size = newSize; if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } modCount++; } return anyToRemove; }
4.2.30、public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator operator) 将该列表的每个元素替换为将运算符应用于该元素的结果。 操作抛出的错误或运行时异常将转发给调用者。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void replaceAll (UnaryOperator<E> operator) { Objects.requireNonNull(operator); final int expectedModCount = modCount; final int size = this .size; for (int i=0 ; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { elementData[i] = operator.apply((E) elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } modCount++; }
4.2.31、public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) 根据指定的比较器对此列表进行排序。
此列表中的所有元素必须使用指定的比较器进行相互比较(即,c.compare(e1,e2)不得为列表中的任何元素e1和e2抛出ClassCastException)。
如果指定的比较器为null,则此列表中的所有元素都必须实现Comparable接口,并且应使用元素的自然顺序。
此列表必须是可修改的,但无需调整大小。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void sort (Comparator<? super E> c) { final int expectedModCount = modCount; Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0 , size, c); if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); } modCount++; }
4.3、ArrayList 方法总结 1)ArrayList 实际上是通过一个数组去保存数据的。当我们构造ArrayList时;若使用默认构造函数,则ArrayList的默认容量大小是10。
2)当ArrayList容量不足以容纳全部元素时,ArrayList会重新设置容量:新的容量=原有容量+(原有容量/2)。
3)ArrayList的克隆函数,即是将全部元素克隆到一个数组中。
4)ArrayList实现java.io.Serializable的方式。当写入到输出流时,先写入“容量”,再依次写入“每一个元素”;当读出输入流时,先读取“容量”,再依次读取“每一个元素”。
5)ArrayList基于数组实现,可以通过下标索引直接查找到指定位置的元素,因此查找效率高,但每次插入或删除元素,就要大量地移动元素,插入删除元素的效率低。
6)在查找给定元素索引值等的方法中,源码都将该元素的值分为null和不为null两种情况处理,ArrayList中允许元素为null。
5、ArrayList toArray() 异常 当我们调用ArrayList中的 toArray(),可能会遇到抛出“java.lang.ClassCastException”异常的情况。
ArrayList提供了2个toArray()函数:
1 2 public Object[] toArray() public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
调用 toArray() 函数会抛出“java.lang.ClassCastException”异常,但是调用 toArray(T[] contents) 能正常返回 T[]。
toArray() 会抛出异常是因为 toArray() 返回的是 Object[] 数组,将 Object[] 转换为其它类型(例如,将Object[]转换为的Integer[])则会抛出“java.lang.ClassCastException”异常,因为Java不支持向下转型。
解决该问题的办法是调用 T[] toArray(T[] contents) , 而不是 Object[] toArray()。
调用 toArray(T[] contents) 返回T[]的可以通过以下几种方式实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static Integer[] toArrayMethod1(ArrayList<Integer> v) { Integer[] newText = new Integer [v.size()]; v.toArray(newText); return newText; } public static Integer[] toArrayMethod2(ArrayList<Integer> v) { Integer[] newText = (Integer[])v.toArray(new Integer [0 ]); return newText; } public static Integer[] toArrayMethod3(ArrayList<Integer> v) { Integer[] newText = new Integer [v.size()]; Integer[] newText2 = (Integer[])v.toArray(newText); return newText2; }
6、ArrayList 遍历方式 6.1、通过迭代器(Iterator)遍历 1 2 3 4 5 List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); Iterator iter = list.iterator();while (iter.hasNext()) { System.out.println(iter.next()); }
6.2、通过索引遍历 由于ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,它支持通过索引值去随机访问元素。
1 2 3 for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.println(list.get(i)); }
6.3、for循环遍历 1 2 3 for (String s:list){ System.out.println(s); }
7、ArrayList 扩容策略 ArrayList底层是使用数组存储 的,当数组大小不足存放新增元素的时候,才会发生扩容 。
在add操作中,ArrayList首先会调用ensureCapacityInternal方法进行扩容 检测的。
如果数组大小不足,则会自动扩容 ;如果扩容后的大小超出 数组最大的大小,则会抛出异常 。
ArrayList扩容策略,主要有两个 步骤:
🌂扩容检测(ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1)):
🌂扩容操作 grow和hugeCapacity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 private static int calculateCapacity (Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } private void ensureCapacityInternal (int minCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity (int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow (int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1 ); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0 ) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0 ) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity (int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0 ) throw new OutOfMemoryError (); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }